How to Use Tines's SOC Automation Capability Matrix



The French information security agency ANSSI reported that Russia-linked APT Nobelium targeted French diplomatic entities. Despite the French agency linked the attacks to the cyberespionage group Nobelium (aka APT29, SVR group, Cozy Bear, Midnight Blizzard, BlueBravo, and The Dukes), ANSSI differentiates these groups into separate threat clusters, including a group named Dark Halo, which was responsible for the 2020 SolarWinds attack.
October 2020, used against high-value targets, most likely for espionage purposes. Western diplomatic entities, such as embassies and Ministries of Foreign Affairs, account for the majority of known victims of Nobelium. However, several IT companies have also reported that they have been targeted by Nobelium’s operators in late 2023 and 2024.
The report published by ANSSI is based upon elements collected by the French agency, evidence shared by its national partners (known as C4 members), and publicly available reports. The document warns of phishing campaigns conducted by Nobelium against French public and diplomatic entities aiming at gathering strategic intelligence.
“Nobelium is characterized by the use of specific codes, tactics, technics and procedures. Most of Nobelium campaigns against diplomatic entities use compromised legitimate email accounts belonging to diplomatic staff, and conduct phishing campaigns against diplomatic institutions, embassies and consulates.” reads the report published by ANSSI. “These activities are also publicly described as a campaign called “Diplomatic Orbiter”.”
Attackers forge lure documents to target diplomatic staff, attempting to deliver their custom loaders to drop public post-exploitation tools such as Cobalt Strike or Brute Ratel C4. The tools allows attackers to access the victim’s network, perform lateral movements, drop additional payloads, maintain persistence, and exfiltrate valuable intelligence.
The agency confirmed that several IT companies have also reported being targeted by Nobelium in late 2023 and 2024.

“French public organisations have been targeted several times by phishing emails sent from foreign institutions previously compromised by Nobelium’s operators.” continues the report. “From February to May 2021, Nobelium operators conducted several phishing campaigns3 exploiting compromised email accounts belonging to the French Ministry of Culture and the National Agency for Territorial Cohesion (ANCT), sending an attachment called “Strategic Review”.”
In March 2022, a European embassy in South Africa received a phishing email that impersonated a French embassy, announcing the closure after a terrorist attack. The attackers sent the email from a compromised account of a French diplomat. In April and May 2022, Nobelium phishing messages reached dozens of email addresses from the French Ministry of Foreign Affair. Threat actors used themes like the closure of a Ukrainian embassy or a meeting with a Portuguese ambassador.
In May 2023, Nobelium targeted several European embassies in Kyiv, including the French embassy, with a phishing campaign involving an email about a “Diplomatic car for sale.” The ANSSI also reported a failed attempt to compromise the French Embassy in Romania.
“ANSSI has observed a high level of activities linked to Nobelium against the recent backdrop of geopolitical tensions, especially in Europe, in relation to Russia’s aggression against Ukraine. Nobelium’s activities against government and diplomatic entities represent a national security concern and endanger French and European diplomatic interests. The targeting of IT and cybersecurity entities for espionage purposes by Nobelium operators potentially strengthens their offensive capabilities and the threat they represent.” concludes the report that also provides indicators of compromise. “Nobelium’s techniques, tactics, and procedures remain mainly constant over time.”
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, ANSSI)


The Biden administration announced it will ban the sale of Kaspersky antivirus software due to the risks posed by Russia to U.S. national security. The U.S. government is implementing a new rule leveraging powers established during the Trump administration to ban the sale of Kaspersky software, citing national security risks posed by Russia.
The Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security banned the Russian cybersecurity firm because it is based in Russia.
Government experts believe that the influence of the Kremlin over the company poses a significant risk,, reported the Reuters. Russia-linked actors can abuse the software’s privileged access to a computer’s systems to steal sensitive information from American computers or spread malware, Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo said on a briefing call with reporters on Thursday.
“Russia has shown it has the capacity and… the intent to exploit Russian companies like Kaspersky to collect and weaponize the personal information of Americans and that is why we are compelled to take the action that we are taking today,” Raimondo said on the call.
This isn’t the first time that Western governments have banned Kaspersky, but the Russian firm has always denied any link with the Russian government.
Reuters reported that the U.S. government plans to add three units of the cybersecurity company to a trade restriction list. The move will significantly impact the company’s sales in the U.S. and potentially in other Western countries that may adopt similar restrictions against the security firm.
TechCrunch reported that the ban will start on July 20, however, the company’s activities, including software updates to its US customers, will be prohibited on September 29.
“That means your software and services will degrade. That’s why I strongly recommend that you immediately find an alternative to Kaspersky,” Raimondo said.
Raimondo is inviting Kaspersky’s customers to replace their software, it also explained that U.S. clients who already use Kaspersky’s antivirus are not violating the law.
“U.S. individuals and businesses that continue to use or have existing Kaspersky products and services are not in violation of the law, you have done nothing wrong and you are not subject to any criminal or civil penalties,” Raimondo added. “However, I would encourage you in the strongest possible terms, to immediately stop using that software and switch to an alternative in order to protect yourself and your data and your family.”
The Department of Homeland Security and the Justice Department will notify U.S. consumers about the ban. They will also set up a website to provide impacted customers with more information about the ban and instructions on the replacement.
The US cybersecurity agency CISA will notify critical infrastructure operators using Kaspersky software to support them in the replacement of the security firm.
In March 2022, the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) added multiple Kaspersky products and services to its Covered List saying that they pose unacceptable risks to U.S. national security.
The Covered List, published by Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau published, included products and services that could pose an unacceptable risk to the national security of the United States or the security and safety of United States persons.
In March 2022, the German Federal Office for Information Security agency, aka BSI, also recommended consumers uninstall Kaspersky anti-virus software. The Agency warns the cybersecurity firm could be implicated in hacking attacks during the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine.
According to §7 BSI law, the BSI warns against using Kaspersky Antivirus and recommends replacing it asap with defense solutions from other vendors.
The alert pointed out that antivirus software operates with high privileges on machines and if compromised could allow an attacker to take over them. BSI remarks that the trust in the reliability and self-protection of a manufacturer as well as his authentic ability to act is crucial for the safe use of any defense software. The doubts about the reliability of the manufacturer, lead the agency in considering the antivirus protection offered by the vendor risky for the IT infrastructure that uses it.
BSI warns of potential offensive cyber operations that can be conducted with the support of a Russian IT manufacturer, it also explains that the vendor could be forced to conduct attacks or be exploited for espionage purposes without its knowledge.
The United States banned government agencies from using Kaspersky defense solutions since 2017, The company rejected any allegation and also clarified that Russian policies and laws are applied to telecoms and ISPs, not security firms like Kaspersky.
In June 2018, the European Parliament passed a resolution that classifies the security firm’s software as “malicious” due to the alleged link of the company with Russian intelligence.
Some European states, including the UK, the Netherlands, and Lithuania also excluded the software of the Russian firm on sensitive systems.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, cyberespionage)
On March 8, 2024, KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive on the consumer data broker Radaris, showing how the original owners are two men in Massachusetts who operated multiple Russian language dating services and affiliate programs, in addition to a dizzying array of people-search websites. The subjects of that piece are threatening to sue KrebsOnSecurity for defamation unless the story is retracted. Meanwhile, their attorney has admitted that the person Radaris named as the CEO from its inception is a fabricated identity.
Radaris is just one cog in a sprawling network of people-search properties online that sell highly detailed background reports on U.S. consumers and businesses. Those reports typically include the subject’s current and previous addresses, partial Social Security numbers, any known licenses, email addresses and phone numbers, as well as the same information for any of their immediate relatives.
Radaris has a less-than-stellar reputation when it comes to responding to consumers seeking to have their reports removed from its various people-search services. That poor reputation, combined with indications that the true founders of Radaris have gone to extraordinary lengths to conceal their stewardship of the company, was what prompted KrebsOnSecurity to investigate the origins of Radaris in the first place.
On April 18, KrebsOnSecurity received a certified letter (PDF) from Valentin “Val” Gurvits, an attorney with the Boston Law Group, stating that KrebsOnSecurity would face a withering defamation lawsuit unless the Radaris story was immediately retracted and an apology issued to the two brothers named in the story as co-founders.
That March story worked backwards from the email address used to register radaris.com, and charted an impressive array of data broker companies created over the past 15 years by Massachusetts residents Dmitry and Igor Lubarsky (also sometimes spelled Lybarsky or Lubarski). Dmitry goes by “Dan,” and Igor uses the name “Gary.”
Those businesses included numerous websites marketed to Russian-speaking people who are new to the United States, such as russianamerica.com, newyork.ru, russiancleveland.com, russianla.com, russianmiami.com, etc. Other domains connected to the Lubarskys included Russian-language dating and adult websites, as well as affiliate programs for their international calling card businesses.
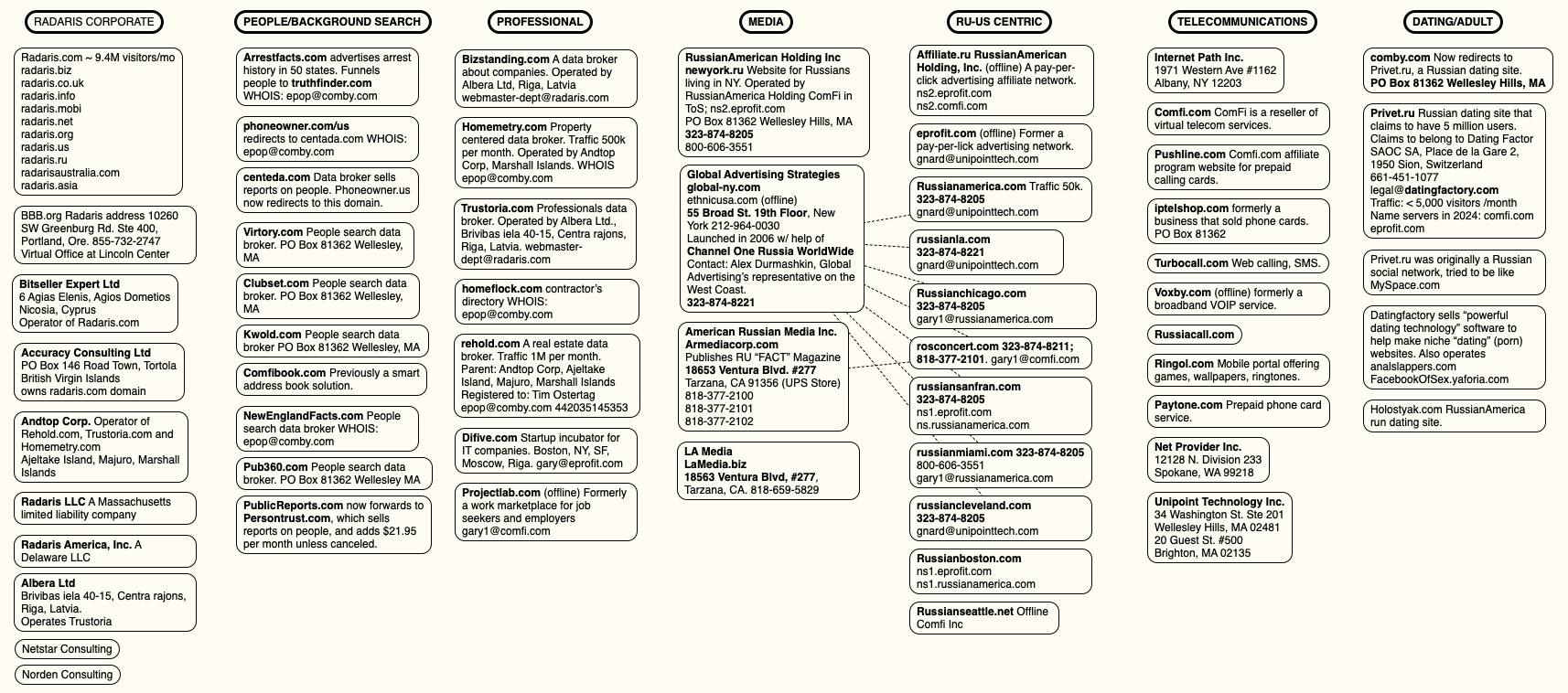
A mind map of various entities apparently tied to Radaris and the company’s co-founders. Click to enlarge.
The story on Radaris noted that the Lubarsky brothers registered most of their businesses using a made-up name — “Gary Norden,” sometimes called Gary Nord or Gary Nard.
Mr. Gurvits’ letter stated emphatically that my reporting was lazy, mean-spirited, and obviously intended to smear the reputation of his clients. By way of example, Mr. Gurvits said the Lubarskys were actually Ukrainian, and that the story painted his clients in a negative light by insinuating that they were somehow associated with Radaris and with vaguely nefarious elements in Russia.
But more to the point, Mr. Gurvits said, neither of his clients were Gary Norden, and neither had ever held any leadership positions at Radaris, nor were they financial beneficiaries of the company in any way.
“Neither of my clients is a founder of Radaris, and neither of my clients is the CEOs of Radaris,” Gurvits wrote. “Additionally, presently and going back at least the past 10 years, neither of my clients are (or were) officers or employees of Radaris. Indeed, neither of them even owns (or ever owned) any equity in Radaris. In intentional disregard of these facts, the Article implies that my clients are personally responsible for Radaris’ actions. Therefore, you intentionally caused all negative allegations in the Article made with respect to Radaris to be imputed against my clients personally.”
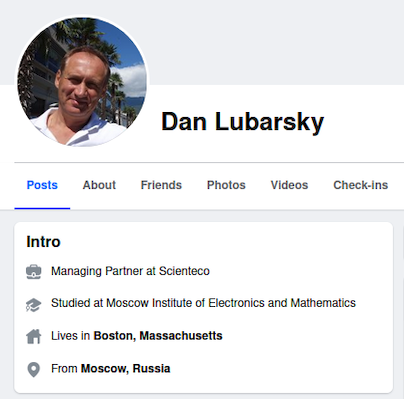
Dan Lubarsky’s Facebook page, just prior to the March 8 story about Radaris, said he was from Moscow.
We took Mr. Gurvits’ word on the ethnicity of his clients, and adjusted the story to remove a single mention that they were Russian. We did so even though Dan Lubarsky’s own Facebook page said (until recently) that he was from Moscow, Russia.
KrebsOnSecurity asked Mr. Gurvits to explain precisely which other details in the story were incorrect, and replied that we would be happy to update the story with a correction if they could demonstrate any errors of fact or omission.
We also requested specifics about several aspects of the story, such as the identity of the current Radaris CEO — listed on the Radaris website as “Victor K.” Mr. Gurvits replied that Radaris is and always has been based in Ukraine, and that the company’s true founder “Eugene L” is based there.
While Radaris has claimed to have offices in Massachusetts, Cyprus and Latvia, its website has never mentioned Ukraine. Mr. Gurvits has not responded to requests for more information about the identities of “Eugene L” or “Victor K.”
Gurvits said he had no intention of doing anyone’s reporting for them, and that the Lubarskys were going to sue KrebsOnSecurity for defamation unless the story was retracted in full. KrebsOnSecurity replied that journalists often face challenges to things that they report, but it is more than rare for one who makes a challenge to take umbrage at being asked for supporting information.
On June 13, Mr. Gurvits sent another letter (PDF) that continued to claim KrebsOnSecurity was defaming his clients, only this time Gurvits said his clients would be satisfied if KrebsOnSecurity just removed their names from the story.
“Ultimately, my clients don’t care what you say about any of the websites or corporate entities in your Article, as long as you completely remove my clients’ names from the Article and cooperate with my clients to have copies of the Article where my clients’ names appear removed from the Internet,” Mr. Gurvits wrote.
The June 13 letter explained that the name Gary Norden was a pseudonym invented by the Radaris marketing division, but that neither of the Lubarsky brothers were Norden.
This was a startling admission, given that Radaris has quoted the fictitious Gary Norden in press releases published and paid for by Radaris, and in news media stories where the company is explicitly seeking money from investors. In other words, Radaris has been misrepresenting itself to investors from the beginning. Here’s a press release from Radaris that was published on PR Newswire in April 2011:
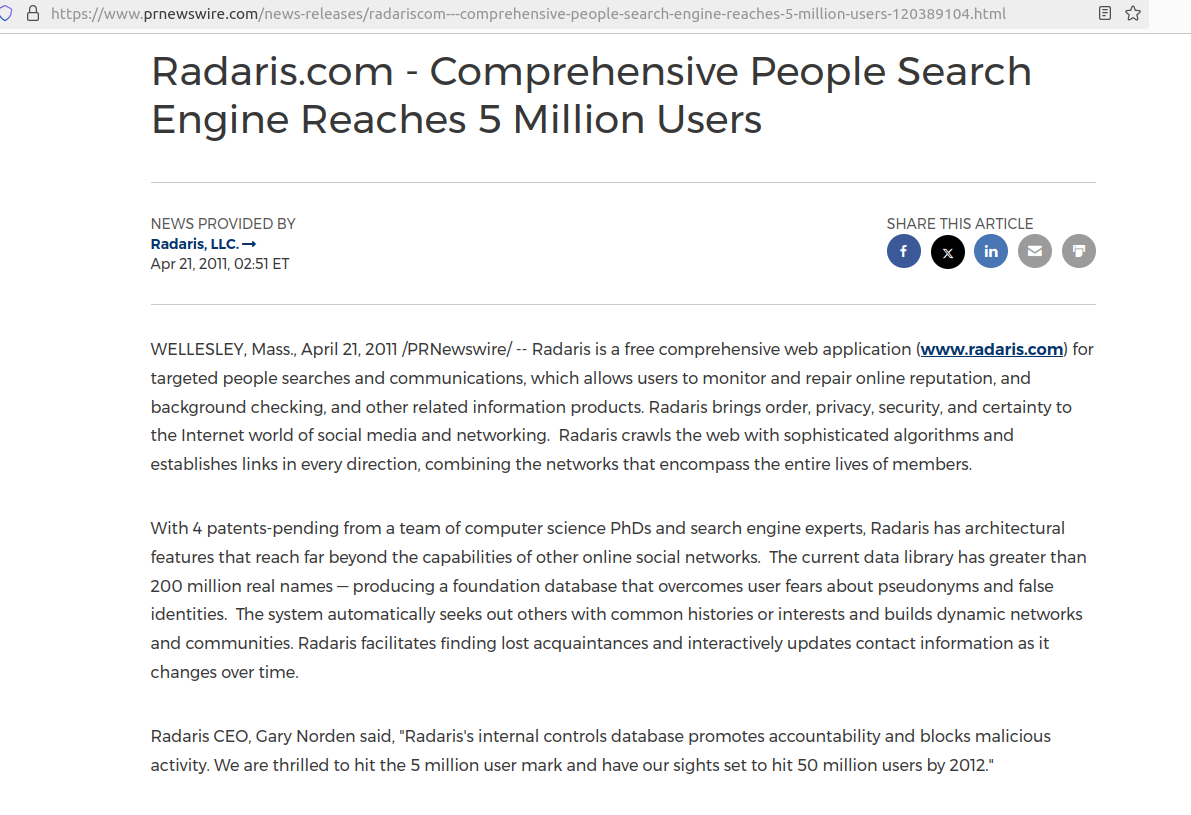
A press release published by Radaris in 2011 names the CEO of Radaris as Gary Norden, which was a fake name made up by Radaris’ marketing department.
In April 2014, the Boston Business Journal published a story (PDF) about Radaris that extolled the company’s rapid growth and considerable customer base. The story noted that, “to date, the company has raised less than $1 million from Cyprus-based investment company Difive.”
“We live in a world where information becomes much more broad and much more available every single day,” the Boston Business Journal quoted Radaris’ fake CEO Gary Norden, who by then had somehow been demoted from CEO to vice president of business development.
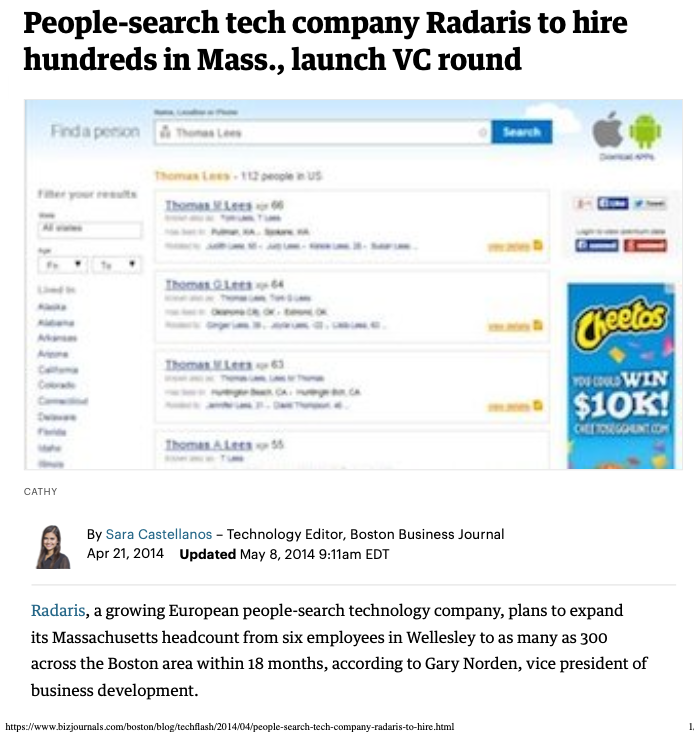
A Boston Business Journal story from April 2014 quotes the fictitious Radaris CEO Gary Norden.
“We decided there needs to be a service that allows for ease of monitoring of information about people,” the fake CEO said. The story went on to say Radaris was seeking to raise between $5 million and $7 million from investors in the ensuing months.
In his most recent demand letter, Mr. Gurvits helpfully included resumes for both of the Lubarsky brothers.
Gary/Dmitry Lubarsky’s resume states he is the owner of Difive.com, a startup incubator for IT companies. Recall that Difive is the same company mentioned by the fake Radaris CEO in the 2014 Boston Business Journal story, which said Difive was the company’s initial and sole investor.
Difive’s website in 2016 said it had offices in Boston, New York, San Francisco, Riga (Latvia) and Moscow (nothing in Ukraine). Meanwhile, DomainTools.com reports difive.com was originally registered in 2007 to the fictitious Gary Norden from Massachusetts.
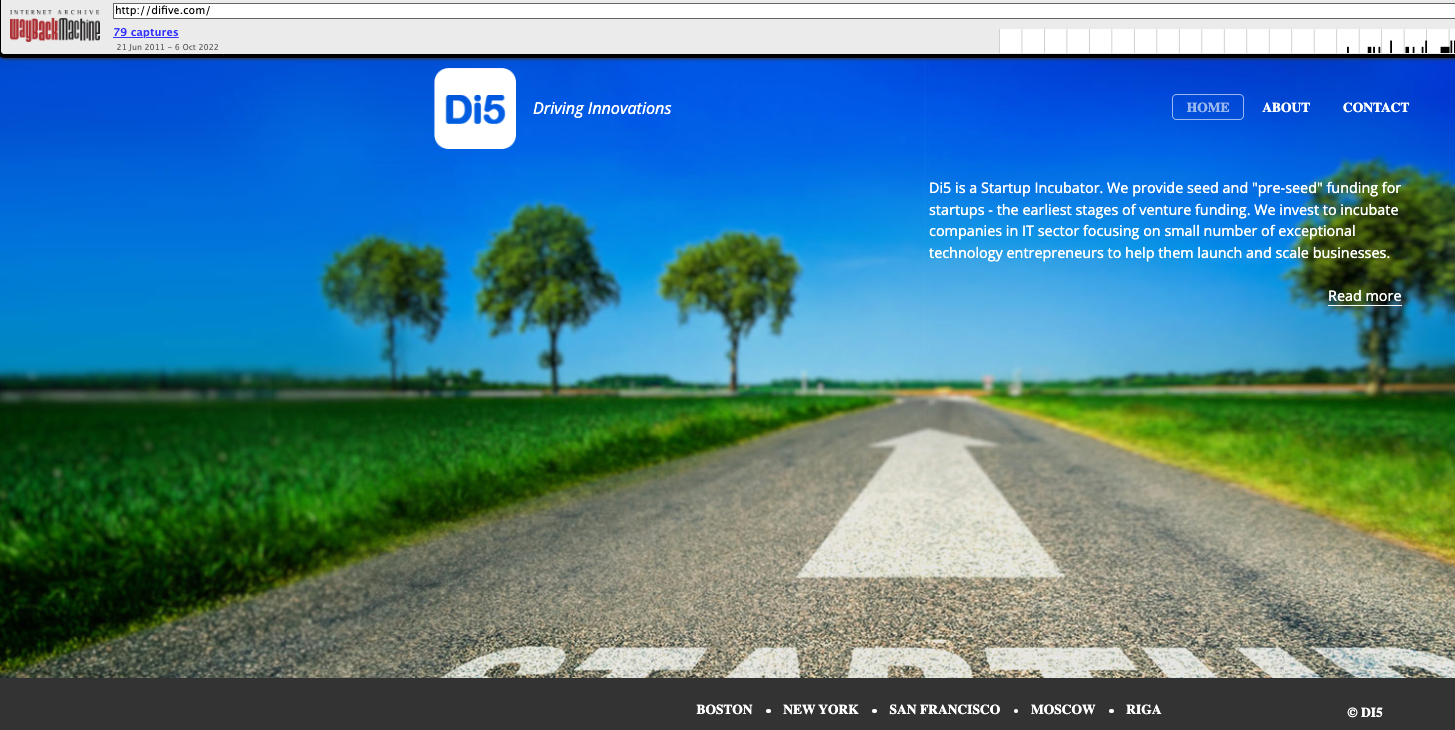
Archived copies of the Difive website from 2017 include a “Portfolio” page indexing all of the companies in which Difive has invested. That list, available here, includes virtually every “Gary Norden” domain name mentioned in my original report, plus a few that escaped notice earlier.
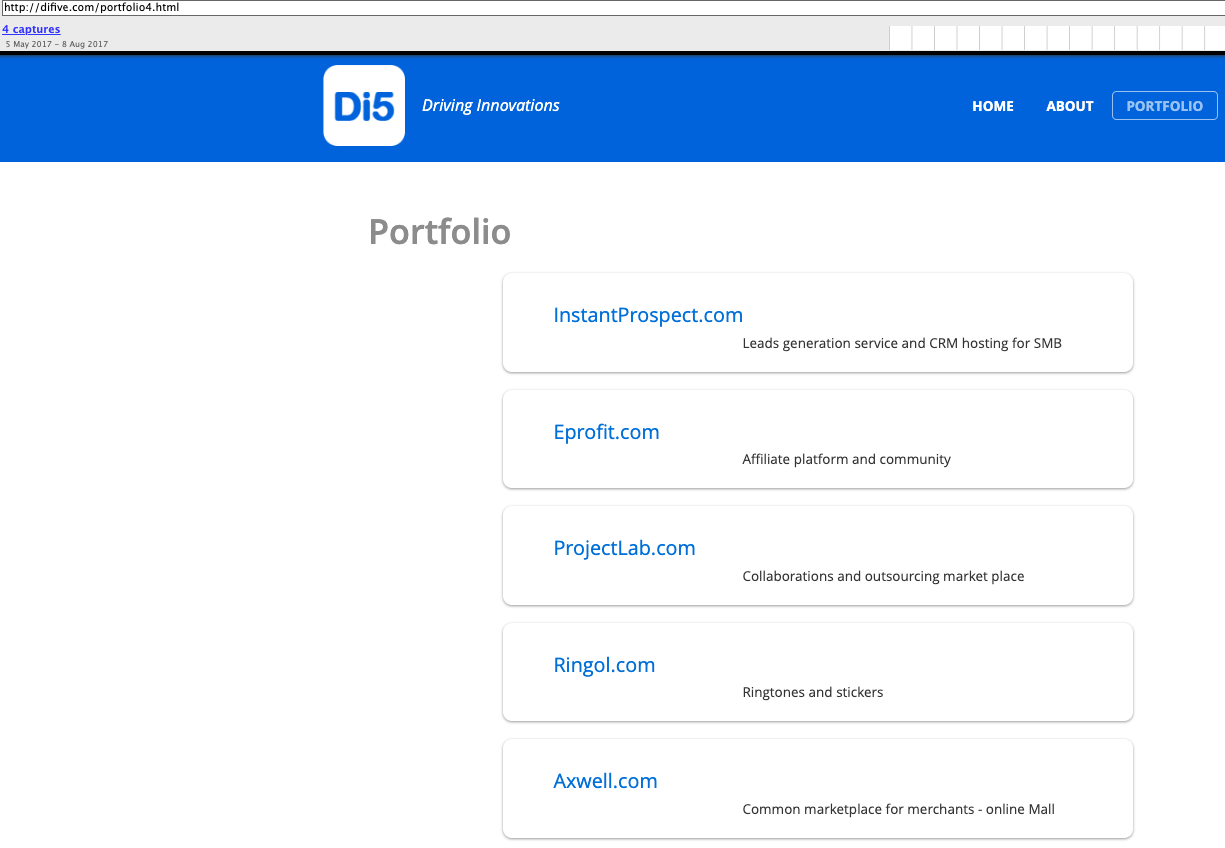
Dan Lubarsky’s resume says he was CEO of a people search company called HumanBook. The Wayback machine at archive.org shows the Humanbook domain (humanbook.com) came online around April 2008, when the company was still in “beta” mode.
By August 2008, however, humanbook.com had changed the name advertised on its homepage to Radaris Beta. Eventually, Humanbook simply redirected to radaris.com.
Astute readers may notice that the domain radaris.com is not among the companies listed as Difive investments. However, passive domain name system (DNS) records from DomainTools show that between October 2023 and March 2024 radaris.com was hosted alongside all of the other Gary Norden domains at the Internet address range 38.111.228.x.
That address range simultaneously hosted every domain mentioned in this story and in the original March 2024 report as connected to email addresses used by Gary Norden, including radaris.com, radaris.ru, radaris.de, difive.com, privet.ru, blog.ru, comfi.com, phoneowner.com, russianamerica.com, eprofit.com, rehold.com, homeflock.com, humanbook.com and dozens more. A spreadsheet of those historical DNS entries for radaris.com is available here (.csv).
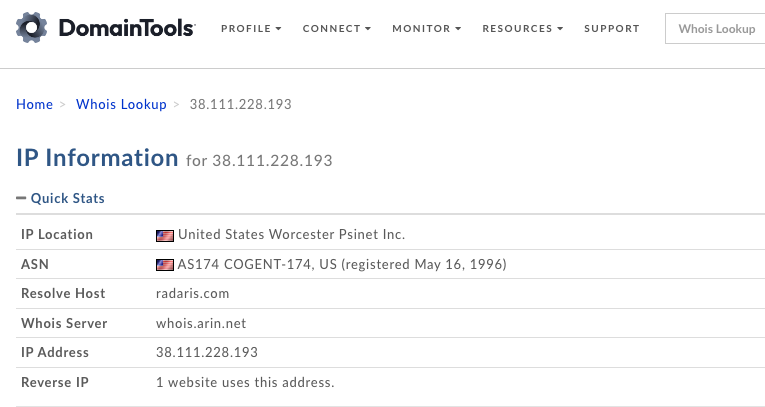
Image: DomainTools.com
The breach tracking service Constella Intelligence finds just two email addresses ending in difive.com have been exposed in data breaches over the years: [email protected], and [email protected]. Presumably, “gn” stands for Gary Norden.
A search on the email address [email protected] via the breach tracking service osint.industries reveals this address was used to create an account at Airbnb under the name Gary, with the last four digits of the account’s phone number ending in “0001.”
Constella Intelligence finds [email protected] was associated with the Massachusetts number 617-794-0001, which was used to register accounts for “Igor Lybarsky” from Wellesley or Sherborn, Ma. at multiple online businesses, including audiusa.com and the designer eyewear store luxottica.com.
The phone number 617-794-0001 also appears for a “Gary Nard” user at russianamerica.com. Igor Lubarsky’s resume says he was the manager of russianamerica.com.
DomainTools finds 617-794-0001 is connected to registration records for three domains, including paytone.com, a domain that Dan Lubarsky’s resume says he managed. DomainTools also found that number on the registration records for trustoria.com, another major consumer data broker that has an atrocious reputation, according to the Better Business Bureau.
Dan Lubarsky’s resume says he was responsible for several international telecommunications services, including the website comfi.com. DomainTools says the phone number connected to that domain — 617-952-4234 — was also used on the registration records for humanbook.net/biz/info/mobi/us, as well as for radaris.me, radaris.in, and radaris.tel.
Two other key domains are connected to that phone number. The first is barsky.com, which is the website for Barsky Estate Realty Trust (PDF), a real estate holding company controlled by the Lubarskys. Naturally, DomainTools finds barsky.com also was registered to a Gary Norden from Massachusetts. But the organization listed in the barsky.com registration records is Comfi Inc., a VOIP communications firm that Dan Lubarsky’s resume says he managed.
The other domain of note is unipointtechnologies.com. Dan Lubarsky’s resume says he was the CEO of Wellesley Hills, Mass-based Unipoint Technology Inc. In 2012, Unipoint was fined $179,000 by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission, which said the company had failed to apply for a license to provide international telecommunications services.
The 2011 Radaris press release quoting their fake CEO Gary Norden said the company had four patents pending from a team of computer science PhDs. According to the resume shared by Mr. Gurvits, Dan Lubarsky has a PhD in computer science.
The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (PTO) says Dan Lubarsky/Lubarski has at least nine technology patents to his name. The fake CEO press release from Radaris mentioning its four patents was published in April 2011. By that time, the PTO says Dan Lubarsky had applied for exactly four patents, including, “System and Method for a Web-Based People Directory.” The first of those patents, published in 2009, is tied to Humanbook.com, the company Dan Lubarsky founded that later changed its name to Radaris.
If the Lubarskys were never involved in Radaris, how do they or their attorney know the inside information that Gary Norden is a fiction of Radaris’ marketing department? KrebsOnSecurity has learned that Mr. Gurvits is the same attorney responding on behalf of Radaris in a lawsuit against the data broker filed earlier this year by Atlas Data Privacy.
Mr. Gurvits also stepped forward as Radaris’ attorney in a class action lawsuit the company lost in 2017 because it never contested the claim in court. When the plaintiffs told the judge they couldn’t collect on the $7.5 million default judgment, the judge ordered the domain registry Verisign to transfer the radaris.com domain name to the plaintiffs.
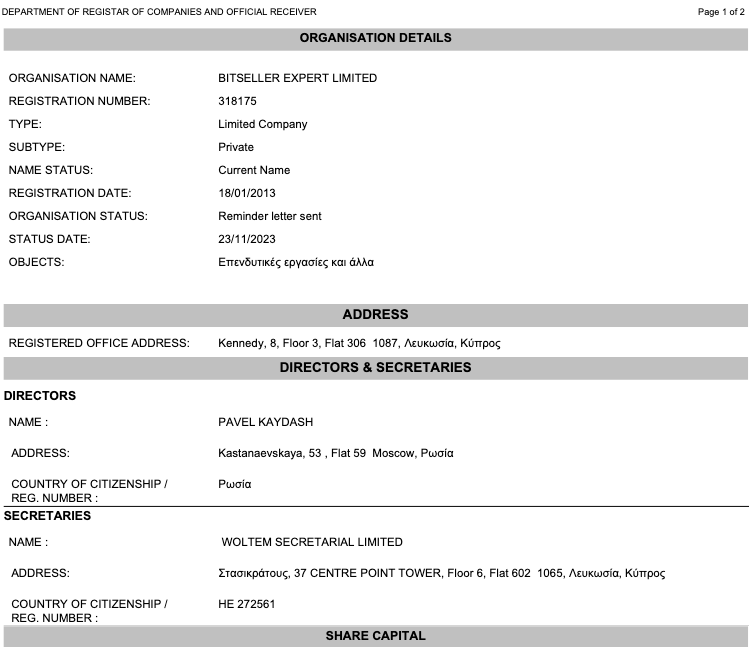
Mr. Gurvits appealed the verdict, arguing that the lawsuit hadn’t named the actual owners of the Radaris domain name — a Cyprus company called Bitseller Expert Limited — and thus taking the domain away would be a violation of their due process rights.
The judge ruled in Radaris’ favor — halting the domain transfer — and told the plaintiffs they could refile their complaint. Soon after, the operator of Radaris changed from Bitseller to Andtop Company, an entity formed (PDF) in the Marshall Islands in Oct. 2020. Andtop also operates the aforementioned people-search service Trustoria.
Mr. Gurvits’ most-publicized defamation case was a client named Aleksej Gubarev, a Russian technology executive whose name appeared in the Steele Dossier. That document included a collection of salacious, unverified information gathered by the former British intelligence officer Christopher Steele during the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign at the direction of former president Donald Trump’s political rivals.
Gubarev, the head of the IT services company XBT Holding and the Florida web hosting firm Webzilla, sued BuzzFeed for publishing the Steele dossier. One of the items in the dossier alleged that XBT/Webzilla and affiliated companies played a key role in the hack of Democratic Party computers in the spring of 2016. The memo alleged Gubarev had been coerced into providing services to Russia’s main domestic security agency, known as the FSB.
In December 2018, a federal judge in Miami ruled in favor of BuzzFeed, saying the publication was protected by the fair report privilege, which gives news organizations latitude in reporting on official government proceedings.
Radaris was originally operated by Bitseller Expert Limited. Who owns Bitseller Expert Limited? A report (PDF) obtained from the Cyprus business registry shows this company lists its director as Pavel Kaydash from Moscow. Mr. Kaydash could not be reached for comment.
Atlassian June 2024 Security Bulletin addressed nine high-severity vulnerabilities in Confluence, Crucible, and Jira products.
The most severe issue addressed by the company is an improper authorization org.springframework.security:spring-security-core dependency in Confluence Data Center and Server. The flaw tracked as CVE-2024-22257 received a CVSS score of 8.2.
The Confluence Data Center and Server update resolved other five SSRF (Server-Side Request Forgery) and DoS vulnerabilities. Below is the list of the addressed flaws:
Confluence Data Center and Server versions 8.9.3, 8.5.11 (LTS), and 7.19.24 (LTS) addressed these vulnerabilities.
Atlassian also fixed a DoS vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-25647, in the Fisheye/Crucible with the release of version 4.8.15.
The software firm also fixed the following vulnerabilities in the Jira Data Center and Server:
| Jira Data Center and Server | 9.12.0 to 9.12.7 (LTS)9.4.0 to 9.4.20 (LTS) | 9.16.0 to 9.16.1 Data Center Only9.12.8 to 9.12.10 (LTS) recommended9.4.21 to 9.4.23 (LTS) | Information Disclosure in Jira Core Data Center | CVE-2024-21685 | 7.4 High |
| Jira Service Management Data Center and Server | 5.15.25.12.0 to 5.12.7 (LTS)5.4.0 to 5.4.20 (LTS) | 5.16.0 to 5.16.1 Data Center Only5.12.8 to 5.12.10 (LTS) recommended5.4.21 to 5.4.23 (LTS) | Information Disclosure in Jira Service Management Data Center and Server | CVE-2024-21685 | 7.4 High |
The company is not aware of attacks in the wild exploiting the vulnerabilities fixed in the June 2024 Security Bulletin.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, China)
The Symantec Threat Hunter Team reported that an alleged China-linked APT group has infiltrated several telecom operators in a single, unnamed, Asian country at least since 2021.
The threat actors used tools associated with Chinese espionage groups, they planted multiple backdoors on the networks of targeted companies to steal credentials.
“The attacks have been underway since at least 2021, with evidence to suggest that some of this activity may even date as far back as 2020. Virtually all of the organizations targeted were telecoms operators, with the addition of a services company that serves the telecoms sector and a university in another Asian country.” reads the report published by Broadcom Symantec Threat Hunter Team.
Evidence collected by the experts suggests that the cluster activity may have been active since 2020.
In a recent espionage campaign, the attackers employed custom malware associated with several Chinese APT groups. Some of the malware used by the threat actors are:
In addition to utilizing custom backdoors. the cyber espionage group also employed a range of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to compromise their targets. They deployed custom keylogging malware, port scanning tools, credential theft through the dumping of registry hives, a publicly available tool known as Responder that acts as a Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution (LLMNR) NetBIOS Name Service (NBT-NS) and multicast DNS (mDNS) poisoner, and enabling RDP.
“Tools used in this campaign have strong associations with multiple Chinese groups and at least three of the custom backdoors deployed are believed to be used exclusively by Chinese espionage actors.” concludes the report.” “The nature of the link between the actors involved in the current campaign remains unclear. Possibilities include, but are not limited to:
The ultimate motive of the intrusion campaign remains unclear.”
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, China)


New Rust-based Fickle Malware Uses PowerShell for UAC Bypass and Data Exfiltration
Fortinet FortiGuard Labs researchers detected a new Rust-based information stealer called Fickle Stealer which spread through multiple attack vectors.
The malware has an intricate code and relies on multiple strategies for its distribution, including VBA dropper, VBA downloader, link downloader, and executable downloader.
Attackers typically download a PowerShell script (u.ps1 or bypass.ps1) to perform initial setup tasks. In some cases, attackers used an additional file to download the PowerShell script.
The main objective of the PowerShell script is to bypass User Account Control (UAC) and execute the Fickle Stealer malware. The script also sets up a task to run another script, engine.ps1, after 15 minutes. The script places a genuine and a fake WmiMgmt.msc file in the system directories to bypass UAC. The fake file abuses an ActiveX control to open a web browser with a local URL that serves a page for downloading and executing Fickle Stealer. This method leverages the Mock Trusted Directories technique to execute with elevated privileges without triggering a UAC prompt.
The scripts u.ps1, engine.ps1, and inject.ps1 frequently report their status by sending messages to the attacker’s Telegram bot. The script does this task downloading and executing tgmes.ps1 with each message. tgmes.ps1, is stored in the Temp folder with a random name and deleted after execution. In addition to messages, tgmes.ps1 sends victim details such as country, city, IP address, OS version, computer name, and user name to the Telegram bot.
Fickle Stealer uses a packer disguised as a legal executable. The experts speculate the author developed the packer by replacing some code of a legal executable with the packer’s code. This trick allows the malicious code to avoid static analysis.
“If the environment check is passed, Fickle Stealer sends victim information to the server. The server sends a list of target applications and keywords as a response.” reads the report. “Fickle Stealer sends all files in folders according to the list.”
The information stealer performs a series of anti-analysis checks to determine if it’s running in a sandbox or a virtual machine environment.
The malware stores stolen data in a specific JSON format that has three key-value pairs:
| {“name”: “RB_{Computer name}”, “title”: {File name}, “body”: {File content}} |
The malware targets crypto wallets, plugins, file extensions, and partial paths, along with applications such as AnyDesk, Discord, FileZilla, Signal, Skype, Steam, and Telegram
Fickle Stealer can steal information from web browsers powered by Chromium and the Gecko browser engine, such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Brave, Vivaldi, and Mozilla Firefox.
“In addition to some popular applications, this stealer searches sensitive files in parent directories of common installation directories to ensure comprehensive data gathering. It also receives a target list from the server, which makes Fickle Stealer more flexible. Variants receiving an updated list are observed. The frequently updated attack chain also shows that it’s still in development.” concludes the report.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, malware)


The security researcher Vsevolod Kokorin (@Slonser) discovered a bug that allows anyone to impersonate Microsoft corporate email accounts. An attacker can trigger the vulnerability to launch phishing attacks.
I want to share my recent case:
— slonser (@slonser_) June 14, 2024
> I found a vulnerability that allows sending a message from any user@domain
> We cannot reproduce it
> I send a video with the exploitation, a full PoC
> We cannot reproduce it
At this point, I decided to stop the communication with Microsoft. pic.twitter.com/mJDoHTn9Xv
The researchers demonstrated the bug exploitation to TechCrunch, Kokorin told TechCrunch that he reported the bug to Microsoft, but the company replied that it couldn’t reproduce his findings. Then Kokorin disclosed the flaw on X.
The researcher explained that the vulnerability works when an attacker sends an email to Outlook accounts.
“Kokorin said he last followed up with Microsoft on June 15. Microsoft did not respond to TechCrunch’s request for comment on Tuesday.” reported TechCrunch. “TechCrunch is not divulging technical details of the bug in order to prevent malicious hackers from exploiting it.”
Kokorin expressed surprise at the reaction to his report, he pointed out that he was only offering assistance to Microsoft.
At this time the issue has yet to be addressed, and it is unclear if any threat actors have already exploited it in attacks in the wild.
We will continue to follow the evolution of this case.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, spoofing)
Resecurity has identified a new activity of Smishing Triad, which has expanded its operations to Pakistan. The group’s latest tactic involves sending malicious messages on behalf of Pakistan Post to customers of mobile carriers via iMessage/SMS. The goal is to steal their personal and financial information.
The code and templates used by the attackers in this smishing kit are consistent with those observed in previous instances of Smishing Triad. Previously, Resecurity described multiple episodes of Smishing Triad activity targeting online banking, e-commerce and payment systems customers in other geographies including USA, EU, UAE and KSA.
Estimating the global scale of threat actors’ activities, our analysts believe they send between 50,000–100,000 messages daily. To achieve this, they leverage stolen databases acquired from the Dark Web, which contain sensitive personal data of citizens including phone numbers. Pakistan, with a population of over 235.8 million, has experienced multiple data breaches in the first half of 2024, compromising the personal identifiable information (PII) of citizens. These records are then processed at scale using automation tools to distribute SMS spam for malicious and fraudulent purposes.
Resecurity observed multiple hosts used by attackers operating smishing kits targeting Pakistan’s postal providers, along with Correos, a state-owned postal provider in Spain, observed in previous episodes of Smishing Triad activity from July 2023. There were identified multiple domain names mapped to the same IP address 23[.]231[.]48[.]129:
Smishing (SMS phishing) attacks can be deceptive and aim to trick individuals into revealing personal information or clicking on malicious links through text messages to compromise digital identity and steal payment data.
The full report is available here:
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Smishing Triad)


Kraken Chief Security Officer Nick Percoco revealed that alleged security researchers exploited a zero-day flaw to steal $3 million worth of cryptocurrency. The researchers are refusing to return the stolen funds.
Kraken Security Update:
— Nick Percoco (@c7five) June 19, 2024
On June 9 2024, we received a Bug Bounty program alert from a security researcher. No specifics were initially disclosed, but their email claimed to find an “extremely critical” bug that allowed them to artificially inflate their balance on our platform.
“Everyday we receive fake bug bounty reports from people claiming to be “security researchers”. This is not new to anyone who runs a bug bounty program. However, we treated this seriously and quickly assembled a cross functional team to dig into this issue.” Percoco explained.
The kraken security team discovered “an isolated bug” that allowed an attacker, under specific circumstances, to initiate a deposit onto the platform and receive funds in their account without fully completing the deposit.
The company pointed out that the client’s assets are not at risk, however, an attacker could effectively print assets in their Kraken account for a while.
The security team addressed the vulnerability within an hour. The vulnerability derived from a recent change in the user interface that would promptly credit client accounts before their assets cleared allowing clients to effectively trade crypto markets in real time.
“This UX change was not thoroughly tested against this specific attack vector.” continues the
After patching the vulnerability, the experts discovered that three accounts exploited the vulnerability within a few days. One of these accounts was verified by an individual claiming to be a security researcher.
Instead, the ‘security researcher’ disclosed this bug to two other individuals who they work with who fraudulently generated much larger sums. They ultimately withdrew nearly $3 million from their Kraken accounts. This was from Kraken’s treasuries, not other client assets.
— Nick Percoco (@c7five) June 19, 2024
Percoco added that the researcher disclosed the bug to two other individuals who used it to withdraw $3 million in stolen funds from their Kraken accounts.
The company requested the researchers to return the stolen funds, but they refused.
Instead, they demanded a call with their business development team (i.e. their sales reps) and have not agreed to return any funds until we provide a speculated $ amount that this bug could have caused if they had not disclosed it. This is not white-hat hacking, it is extortion!
— Nick Percoco (@c7five) June 19, 2024
“This is not white-hat hacking, it is extortion!” said Percoco, who added that his company notified law enforcement.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, zero-day)
Google has issued a Chrome 126 security update, addressing six vulnerabilities, including a flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-6100 which was demonstrated during the SSD Secure Disclosure’s TyphoonPWN 2024. TyphoonPWN is a live hacking competition held annually at TyphoonCon, an Offensive Security Conference in Seoul, South Korea.
The vulnerability is a high-severity type confusion issue in the V8 script engine that was reported by Seunghyun Lee (@0x10n) participating in SSD Secure Disclosure’s TyphoonPWN 2024 on 2024-06-04
Lee received a $20,000 bug bounty reward for reporting the issue.
Google also addressed the following issues:
Google hasn’t shared technical details on the vulnerabilities, the good news is that the company is not aware of attacks in the wild exploiting the flaws addressed by the Chrome 126 security update.
Chrome 126 security update is now rolling out to users as version 126.0.6478.114 for Linux and as versions 126.0.6478.114/115 for Windows and macOS.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Google)


AMD has launched an investigation after the threat actor IntelBroker announced they were selling sensitive data allegedly belonging to the company.
“We are aware of a cybercriminal organization claiming to be in possession of stolen AMD data,” the chip maker told media outlets. “We are working closely with law enforcement officials and a third-party hosting partner to investigate the claim and the significance of the data.”
Earlier this week IntelBroker announced on the BreachForums cybercrime forum that they were “selling the AMD.com data breach.”
The seller states that the files were stolen in June 2024.

The allegedly stolen data includes information on future products, datasheets, employee and customer databases, property files, firmware, source code, and financial documentation.
The seller claims compromised employee data includes first and last names, job functions, business phone numbers, email addresses, and status.
It’s unclear if the data is authentic and which it the source.
IntelBroker recently made the headlines because he attempted to sell data from Europol and Zscaler.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, AMD)



Researchers at Datadog uncovered a new cryptojacking campaign linked to the attackers behind Spinning YARN campaign.
The threat actors target publicly exposed and unsecured Docker API endpoints for initial access.
The attack begins with the threat actor scanning the internet to find hosts with Docker’s default port 2375 open. After locating a valid host, they perform Docker reconnaissance by querying the Docker host’s version using the docker version command. Following this confirmation, the attacker starts the exploitation phase by attempting to create an Alpine Linux container and using Docker’s Binds parameter to map the host’s root directory (/) to a directory within the container (/mnt). Below is the command snippet used in the campaign:
"Image": "alpine",
"HostConfig": {
"Binds": ["/:/mnt"]
}If this step is successful, the attacker gains access to the Docker host’s underlying filesystem through the /mnt directory inside the container, allowing them to escalate their privileges.
In addition to defining the container image and host configuration parameters, the attacker executes a shell command within the container itself to set the root of subsequent processes.
The attackers were observed deploying multiple payloads, including chkstart) that downloads and executes additional malicious payloads and a tool to perform lateral movement (exeremo) used to propagate the malware via SSH.
The threat actors used a a shell script named “vurl” to retrieve the malicious payloads from a server under their control. The script includes another shell script called “b.sh” that, in turn, packs a Base64-encoded binary named “vurl” and is also responsible for fetching and launching a third shell script known as “ar.sh” (or “ai.sh”).
“After the attacker gains initial access and achieves execution via cron, the next stage of the campaign is to fetch and execute a new shell script—b.sh. This script contains a base64-encoded tar archive of a new binary named vurl. The script decodes and extracts this binary to /usr/bin/vurl, overwriting the existing shell script version, before fetching and executing one of two shell scripts—ar.sh or ai.sh.” reads the report published by the researchers.
The attackers use an unusual persistence mechanism by modifying existing systemd services and using the ExecStartPost configuration option to execute malicious commands.
The shell script “ar.sh” is used for multiple purposes including setting up a working directory, installing tools to scan the internet for vulnerable hosts, remove existing cron entries, weaken the system by disabling firewalls, clearing shell history, and preventing new lines from being added to the history file.
The script is ultimately used to fetch the next-stage payload “chkstart.”
Attackers used Golang binary, such as vurl, to set up a remote access and download additional tools from a remote server. The experts observed attackers downloading “m.tar,” and an XMRig miner called “top,”.
“This update to the Spinning YARN campaign shows a willingness to continue attacking misconfigured Docker hosts for initial access. The threat actor behind this campaign continues to iterate on deployed payloads by porting functionality to Go, which could indicate an attempt to hinder the analysis process, or point to experimentation with multi-architecture builds.” concludes the report.
“Although the likely objective of this campaign is to deploy an XMRig miner to compromised hosts, the attackers also ensured that they maintain access to victim machines via SSH. Maintaining remote code execution to victim hosts could mean that attackers can leverage their access for additional objectives”
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Docker)

VMware addressed multiple vCenter Server vulnerabilities that remote attackers can exploit to achieve remote code execution or privilege escalation.
vCenter Server is a centralized management platform developed by VMware for managing virtualized environments.
The vCenter Server contains multiple heap-overflow flaws, tracked as CVE-2024-37079, CVE-2024-37080 (maximum CVSSv3 base score 9.8), in the implementation of the DCERPC protocol.
“A malicious actor with network access to vCenter Server may trigger these vulnerabilities by sending a specially crafted network packet potentially leading to remote code execution.” reads the advisory published by the company.
Customers are recommended to install the released security patches, no workarounds are available.
The vulnerabilities were reported by Hao Zheng (@zhz) and Zibo Li (@zbleet) from TianGong Team of Legendsec at Qi’anxin Group.
VMware also addressed multiple local privilege escalation vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2024-37081 (maximum CVSSv3 base score of 7.8), in the vCenter Server.
“The vCenter Server contains multiple local privilege escalation vulnerabilities due to misconfiguration of sudo.” reads the advisory. “An authenticated local user with non-administrative privileges may exploit these issues to elevate privileges to root on vCenter Server Appliance.”
The issue was reported by Matei “Mal” Badanoiu from Deloitte Romania
VMware confirmed that it is not aware of attacks in the wild exploiting these issues.
The following table reports impacted products and fixed versions:
| VMware Product | Version | Running On | CVE | CVSSv3 | Severity | Fixed Version | Workarounds | Additional Documentation |
| vCenter Server | 8.0 | Any | CVE-2024-37079, CVE-2024-37080, CVE-2024-37081 | 9.8, 9.8, 7.8 | Critical | 8.0 U2d | None | FAQ |
| vCenter Server | 8.0 | Any | CVE-2024-37079, CVE-2024-37080 | 9.8, 9.8 | Critical | 8.0 U1e | None | FAQ |
| vCenter Server | 7.0 | Any | CVE-2024-37079, CVE-2024-37080, CVE-2024-37081 | 9.8, 9.8, 7.8 | Critical | 7.0 U3r | None | FAQ |
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, VMware)